- Home
- pen and cage culture
- Coastal aqua culture- pond culture; Open sea- cage culture Shellfish culture- Off bottom, bottom Culture methods- Rafts, long lines and stakes pond culture. - ppt download
Coastal aqua culture- pond culture; Open sea- cage culture Shellfish culture- Off bottom, bottom Culture methods- Rafts, long lines and stakes pond culture. - ppt download
4.5 (753) · $ 24.50 · In stock
Site selection Based on the species to be cultured and technology to be adopted Points to consider- Agro chemical conditions, access to market, roads and communication, protection from natural disaster, labour availability, public utilities Meteorological and hydrological information, soil characteristics, quantity and quality of available water, ease of filling and drainage Astronomical information- tides Land slope- not more than 2%- good Extensive area- for future expansion and farm facilities Pollution, legal and social aspects, environmental constraints
Coastal aqua culture- pond culture; Open sea- cage culture Shellfish culture- Off bottom, bottom Culture methods- Rafts, long lines and stakes pond culture Raft culture
Salinity of 10 t0 35 ppt (optimum would depend on the species selected for culture) Brackish/seawater of good quality and high natural productivity- optimum water quality will depend on the species to be cultured. Away from all sources of pollution (urban, agricultural and industrial). Low flood risk Land of suitable elevation to enable easy drainage of water from the ponds Clay or clayey loam soil Soil with relatively higher pH (>6.0) Good electricity connection and supply Good availability of labour Road and transportation Availability of communication Availability of supplies Proximity to markets Availability of seed for stocking.
Design Site physiography, source and nature of water supply, type of stock enclosure to be used, organisms to be cultured and techniques of management Seasonal variation in salinity of available water and availability of fresh water Tidal ponds- information on tides, ground elevation Size and shape- imp- quantity of water & extent of land available, technology to be followed (extensive, semi intensive or intensive)
Water supply system Quantity of water- depend on soil and climatic conditions Water supply- also depends on species to be cultured Separate supply of water and drainage canals, separate inlets and outlets for operational safety and efficiency
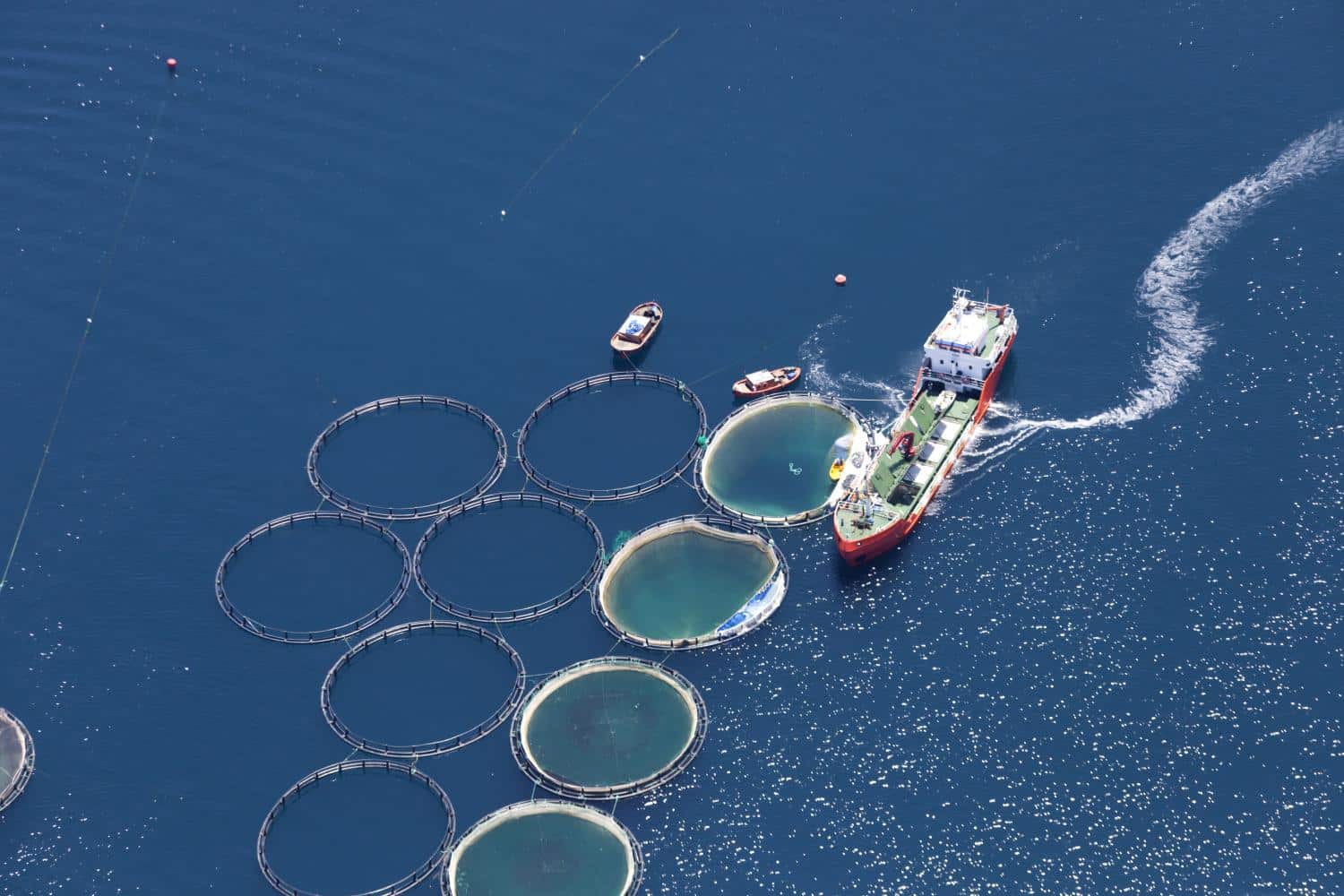
Originated in kampuchea Salmons- Norway; yellowtail- Japan; Groupers and sea bass- in Hong Kong and Singapore Floating unit, a framework & flexible mesh net suspended under it Floating units- Styrofoam, Polyethylene pipes or ready made pontoons of plastics or metal
Framework- impregnated wood, bamboo spars, galvanized scaffoldings or welded aluminum bars Nylon –net; weldmesh or even woven split bamboo is also used Cage flotillas - provide sager working conditions and enable storage of feed on site, as well as installation of automatic feeder
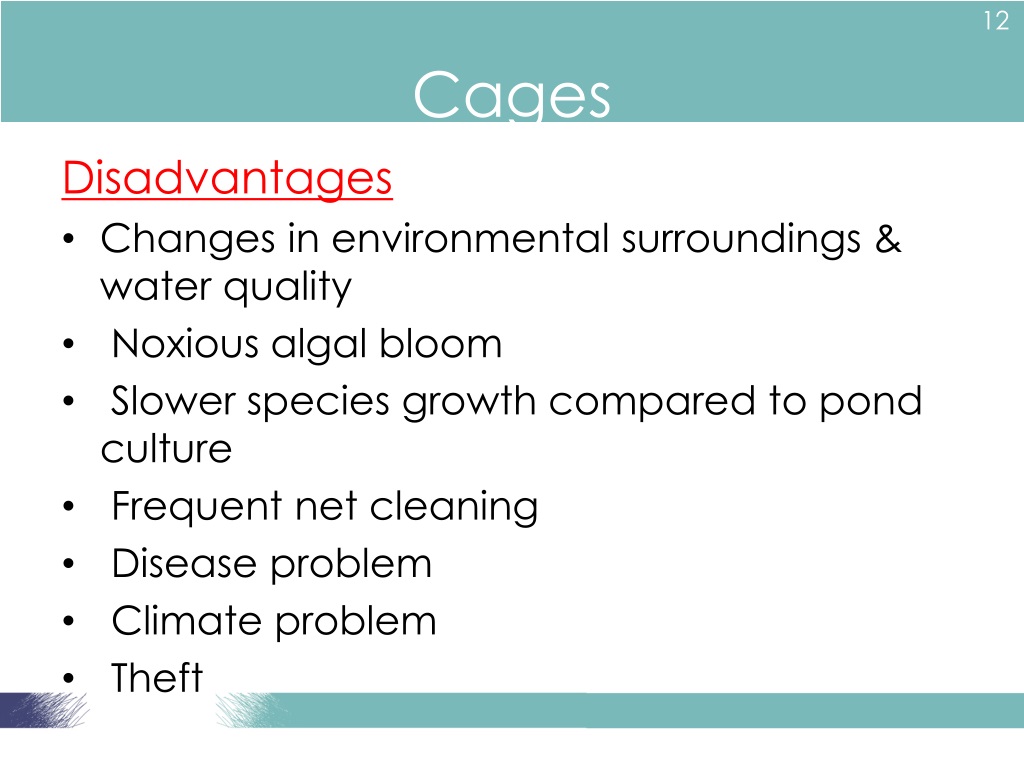
Accumulated wastes-decompose -oxygen depletion or generation of methane or other toxic gasses under anaerobic conditions Cages also increase deposition of silt on the bottom of the site So, important to have enough movement of clean water below the floating cages Carrying capacities -avoid overcrowding of cages.
S simple unit holds a net of four vertical sides and is rectangular in cross section Mooring cages to a jetty with direct access to a quay, in order to facilitate work and reduce labour cost Feed dispensers are installed above each cage; or, manual feeding has to be done Most of the presently available cages are designed for use in protected bays and fjords In order to utilize more open waters and high seas, special cages with a flexible rubber framework have recently been developed..
Pens - transitional structures between ponds and cages Yellowtail in Japan, milkfish in the Philippines and salmon in Norway – use pen culture The success of pens - hydrobiological conditions of the site The design- base on - adequate knowledge of water quality, floods, waves and currents and prevalence of predatory animals
Pens - formed by net barriers to partition off areas of an open water body, such as intertidal areas of the sea, bays or lagoons Enclosure is formed one side of the shore and on the other three by a wall of nylon netting hung from pole driven into the bottom Net barriers may be hung from steel cables stung between the poles or the concrete of steel piles
As a further precaution to prevent fish escaping heavy rubble is piled up at the bottom.
Oyster spats are sowed and harvested when grown to marketable size- cheaper, but siltation over oysters beds can cause problems.
Off-bottom culture: 1.Pole /stick culture: Wooden or bamboo sticks are installed in rows in shallow muddy regions of the intertidal zones Sheltered areas free from strong waves, wood boring organisms are selected Seed oysters are attached to the poles using degradable nets, or sting on which oysters are collected are strewn round the poles for fattening and final harvest Pole /stick culture
Raft/string culture: – string/trays are suspended from floating rafts or long lines – Raft are use in protected areas, strings in more exposed areas – Rafts/longlines are supported by buoys – Trays are made of wood or wire screens – Spat oysters are placed in trays and suspend for grow out Raft/string culture.
The culture frames are suspended in the sub-littoral zone from poles driven into the bottom in such a way that the flat surface of the net is close to water surface even during low tides. Fragments of plants are twisted into the ropes and allowed to grow to harvestable quantity.
PPT - PRINCIPLES OF AQUACULTURE (AKU3201) PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:9457923

Coastal aqua culture- pond culture; Open sea- cage culture Shellfish culture- Off bottom, bottom Culture methods- Rafts, long lines and stakes pond culture. - ppt download

The Definitive Guide to Aquaculture

Seaweeds cultivation methods and their role in climate mitigation and environmental cleanup - ScienceDirect

Coastal aqua culture- pond culture; Open sea- cage culture Shellfish culture- Off bottom, bottom Culture methods- Rafts, long lines and stakes pond culture. - ppt download

Farming freshwater prawns

PPT - PRINCIPLES OF AQUACULTURE (AKU3201) PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:9457923

Assessment of long-term effects from cage culture practices on heavy metal accumulation in sediment and fish - ScienceDirect

Types of Aquaculture practices

Offshore and Multi-Use Aquaculture with Extractive Species: Seaweeds and Bivalves

PDF) Cover: Line drawings of commercial aquatic species produced through capture-based aquaculture. Drawings from the FAO Species Identification and Data Programme (SIDP). Montage created

4. AQUACULTURE METHODS AND PRACTICES: A SELECTED REVIEW












